Best Tympanoplasty Surgery Cost in India
How Much Does Tympanoplasty Surgery cost in India?
The Average cost of Tympanoplasty Surgery in India ranges between 1500-2500 USD. Its depends in hospital locations and surgeon experience.
What Is tympanoplasty?
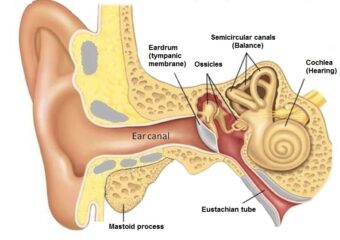
A tympanoplasty is the surgical repair of a hole in the eardrum, which is known as a perforated eardrum. It is an inpatient procedure done under general anesthesia (or sometimes under local anesthesia), and takes two hours or more. Tympanoplasty is often done in children, but adults may in some cases require the procedure as well. Here’s everything you need to know before going in for your procedure.
In a tympanoplasty, the surgeon patches a hole within the eardrum that isn’t healing by itself. The surgery is done either through the ear canal or through an incision at the back of the ear. A tissue graft is taken from the patient, usually from behind the ear, and used as the patch. A synthetic material graft may be used also. It is held in place with packing material.
Why Is a Tympanoplasty Done?
Doctors do a tympanoplasty when the eardrum (or tympanic membrane) has a hole that doesn’t close on its own. It is done to improve hearing and prevent water from getting into the middle ear.
- Kids can get a hole in an eardrum from:
- infections that cause the eardrum to burst
- ventilation (ear) tubes that fall out or are removed
- injury, such as puncturing the eardrum with a cotton swab
- cholesteatoma, a growth within or behind the eardrum
Most of the time, the eardrum can repair itself. So at first, doctors closely watch a hole in a child’s eardrum rather than fix it right away. They might wait years to repair one in a very young child. This lets the ear develop enough to help prevent complications after the surgery. Surgery might also wait if a child has ongoing problems with ear infections.
When is tympanoplasty in children recommended?
Pediatric tympanoplasty is a procedure performed to repair a perforated eardrum in a child’s ear. An eardrum perforation is simply a hole in the eardrum (tympanic membrane). The eardrum is a thin membrane deep in our ear canal. This membrane vibrates when sound waves hit it and helps transfer sound energy into the inner ear which allows us to hear.
A hole in the eardrum can come from a bad ear infection, a surgical procedure like placement of an ear tube, or from trauma such as jabbed deep inside the ear canal (one of many reasons to avoid using any cotton swab to clean your ears!) Tympanoplasty surgery is a common way to repair the perforation, if necessary.
What are the indications for a tympanoplasty?
This procedure is usually not performed (or needed) in children under four years of age. A tympanoplasty is recommended when the eardrum is torn (perforated), sunken in (atelectatic), or otherwise abnormal and associated with hearing loss. Abnormalities of the ear drum and middle ear bones can occur through injury, OTITIS MEDIA, congenital (at birth) deformities, or chronic ear conditions such as a CHOLESTEATOMA.
What are the Symptoms of tympanoplasty?
Signs and symptoms of a tympanoplasty may include:
- Ear pain that may subside quickly
- Mucuslike, pus-filled or bloody drainage from your ear
- Hearing loss
- Ringing in your ear (tinnitus)
- Spinning sensation (vertigo)
- Nausea or vomiting that can result from vertigo
What are the diagnosis need?
Your family doctor or ENT specialist can often determine if you have a ruptured (perforated) eardrum with a visual inspection using a lighted instrument (otoscope or microscope).
He or she may conduct or order additional tests to determine the cause of your ear symptoms or to detect the presence of any hearing loss. These tests include:
- Laboratory tests. If there’s discharge from your ear, your doctor may order a laboratory test or culture to detect a bacterial infection of your middle ear.
- Tuning fork evaluation. Tuning forks are two-pronged, metal instruments that produce sounds when struck. Simple tests with tuning forks can help your doctor detect hearing loss.
- A tuning fork evaluation may also reveal whether hearing loss is caused by damage to the vibrating parts of your middle ear (including your eardrum), damage to sensors or nerves of your inner ear, or damage to both.
- Tympanometry. A tympanometer uses a device inserted into your ear canal that measures the response of your eardrum to slight changes in air pressure. Certain patterns of response can indicate a perforated eardrum.
- Audiology exam. This is a series of strictly calibrated tests that measure how well you hear sounds at different volumes and pitches. The tests are conducted in a soundproof booth.
Before tympanoplasty Surgery?
During your first visit to the doctor, medical history will be obtained. The history and details of the severity of otalgia, hearing loss, vertigo, duration of the perforation or previous attempt at repair will also be obtained. The doctor may also ask about the history of recent infection, and frequency and number of infections. Pneumatic otoscopy and otomicroscopy will be done as a part of physical examination.
Before the surgery, acute or chronic ear infection (if any) will be treated. If the surgery is planned to be done under general anaesthesia, then you will be asked to stop eating before 8 hours of the procedure. Avoid taking any medication that contains aspirin or ibuprofen a week before the surgery.
During the Procedure
You will be given local or general anesthesia to numb the area of operation or to put you to sleep. The kind of tympanoplasty procedure will be chosen depending on the severity of the defect. If the perforation is small, a small incision will be made into the ear canal and the remaining eardrum will be uplifted away from the canal. The surgeon uses a microscope to enlarge the view of the structure to perform the operation.
However, if the hole is large, the incision is made behind the ear, which brings the entire ear forward and gives the surgeon a full access to the perforation. The perforated remnant is then rotated forward to get a clear view of the bones of hearing. The scar tissues are removed from a laser or micro hooks and the remaining tissues are taken from the tragus, the back of the ear or from a vein. Once done, an absorbable gelatin sponge is used to support the graft, which is then inserted under the remaining remnant and in the perforation to fill the gap. In order to place the graft in its place and prevent it from sliding, a very thin sheeting is placed over the graft, so that it won’t slide out when the patient sneezes. The incision is then closed with stitches and a sterile patch is positioned outside the ear canal.
What can I expect after surgery?
A patch myringoplasty usually takes 10 to 15 minutes. Tympanoplasty in children can take 1 to 2 hours. Your doctor will talk to you as soon as the surgery is over.
Your child will wake up in the recovery room after surgery. This may take 45 minutes to an hour. When your child is awake, he or she will be taken to the Short Stay post operative area to complete the recovery. You can be with your child once he or she has been transferred to this area.
Children can almost always go home the same day of surgery. In rare cases an overnight stay may be necessary (e.g., your child has excessive nausea or vomiting). If your child does stay overnight, one parent is required to stay overnight too.
Your child may have bloody discharge or drainage from the ear canal for a few days after surgery. This is normal and is no cause for alarm.
Ear pain and soreness are also common after surgery. These symptoms should go away during the first 3 to 5 days after surgery. Your doctor may prescribe pain medicine to take home for the first few days after surgery.
What are the risks and complications of a tympanoplasty?
Because this surgery takes place in and around the ear, there are special risks for this surgery in addition to the usual risks of infection and bleeding. Because each child’s situation is different, your Pediatric ENT surgeon will relate to you just how likely these complications are to occur.
- HEARING LOSS – A tympanoplasty is performed to help restore normal hearing. However, some hearing loss (more common with ossiculoplasty) may still be present after the procedure. An operation is termed successful if the hearing is restored within 10-15 decibels of normal.
- FACIAL NERVE INJURY AND PARALYSIS – Because the facial nerve runs close to the surgical site, injury although uncommon, can occur. This may result in temporary facial muscle weakness and/or loss of taste on one side of the tongue.
- DIZZINESS – This complication after surgery is rare and is more likely to occur when MASTOIDECTOMY is performed for CHOLESTEATOMA when the cholesteatoma has eroded the balance system.
- LOSS OF GRAFT – Because this operation involves grafting using your child’s own tissue, very rarely this tissue will not survive long enough for the hole in the eardrum to heal completely. In this case, another operation may be necessary. Because the success rate of this surgery is so high, re-operation also has a very high success rate.
Frequently asked questions about tympanoplasty Surgery?
Q. How successful is tympanoplasty in restoring normal hearing?
A. Return to a normal range of hearing after tympanoplasty is dependent upon the extent of the abnormality. Surgeries that involve repair of the eardrum only usually have a success rate of 85-90%. A second operation may be necessary in some cases if the hearing is not restored to an acceptable level.
Q. How long does it take to recover from a tympanoplasty?
A. Full tympanoplasty surgery recovery time can be 2 to 3 months. In fact, the hearing will probably be worse than it was before surgery until this packing dissolves. At the first postoperative visit, your doctor may gently clean the ear canal with a vacuum in order to inspect the reconstructed eardrum.
Best Tympanoplasty Surgeons in India
- Dr. Atul Mittal
- Dr. Anish Gupta
- Dr. Shahshidhar
- Dr. K.K. Handa
- Dr. Sanjay Sachdeva
- Dr. Harpreet Singh
- Dr-W.V.B.S-Ramalingam
- Dr. Ameet Kishore
- Dr. Arvind-Soni
- Dr. Aru Chhabra Handa
Best Tympanoplasty Hospitals in India
- Fortis Memorial Research Institute
- Medanta The Medicity
- Artemis Hospital
- Apollo Hospitals
- Max Hospitals
- Manipal Hospitals
- BLK super Specialty Hospital
- Narayana Superspeciality Hospital
- W Pratiksha Hospital
- Jaypee Hospital
