Breast Cancer Treatment Cost In India

How Much Does Breast Cancer Treatment Cost In India?
The cost of breast cancer treatment in India can vary depending on several factors such as the stage of cancer, the type of treatment required, the hospital, the location, and the individual patient’s medical needs. It’s important to note that the following cost estimates are approximate and can vary significantly:
- Diagnostic Tests: The initial diagnostic tests for breast cancer, including mammography, ultrasound, biopsy, and blood tests, may cost around ₹5,000 to ₹20,000 (Indian Rupees), which is approximately $70 to $280 US dollars.
- Surgery: The cost of breast cancer surgery depends on the type of surgery performed, such as lumpectomy, mastectomy, or breast reconstruction. Surgical expenses can range from ₹1,50,000 to ₹4,00,000 (Indian Rupees), approximately $2,100 to $5,600 US dollars.
- Radiation Therapy: The cost of radiation therapy for breast cancer treatment can vary based on the number of sessions required. On average, the cost can range from ₹1,50,000 to ₹4,00,000 (Indian Rupees), approximately $2,100 to $5,600 US dollars.
- Chemotherapy: The cost of chemotherapy for breast cancer depends on the type of drugs used and the duration of treatment. The estimated cost per cycle can range from ₹10,000 to ₹1,00,000 (Indian Rupees), approximately $140 to $1,400 US dollars. Multiple cycles are usually required.
- Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy: These treatments, such as Herceptin (trastuzumab) and immunotherapy drugs, may be recommended based on the specific characteristics of the breast cancer. The cost can vary but is generally higher than chemotherapy, ranging from ₹50,000 to ₹5,00,000 (Indian Rupees) per cycle, approximately $700 to $7,000 US dollars.
- Hormone Therapy: Hormone therapy, often prescribed for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer, may involve taking medications for several years. The cost can vary, but on average, it can range from ₹10,000 to ₹50,000 (Indian Rupees) per month, approximately $140 to $700 US dollars.
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider or directly contact hospitals and clinics in India for accurate and up-to-date cost estimates for breast cancer treatment. Additionally, health insurance coverage, government schemes, and hospital-specific packages may also influence the final cost.
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the breast tissue. It can affect both men and women, but it is much more common in women.
Breast cancer usually begins in the cells that line the milk ducts or lobules of the breast. It can spread to other parts of the body if not detected and treated early. Common symptoms of breast cancer include a lump in the breast, changes in breast size or shape, nipple discharge, or changes in the skin on the breast.
There are several types of breast cancer, including ductal carcinoma in situ, invasive ductal carcinoma, and inflammatory breast cancer. Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or hormone therapy, depending on the type and stage of the cancer.
Breast cancer is usually diagnosed through a combination of physical exams, imaging tests, and biopsy. Early detection is important for successful treatment, so it’s recommended that women perform regular self-exams and get mammograms as recommended by their healthcare provider.
What Are the Symptoms of Breast Cancer?
The symptoms of breast cancer may vary from person to person and can be different for different types of breast cancer. Some of the common signs and symptoms of breast cancer include:
- A lump or thickening in the breast or armpit.
- Pain or tenderness in the breast.
- Change in size or shape of the breast.
- Change in the skin texture, such as dimpling or puckering.
- Redness or rash on the breast or nipple.
- Nipple discharge or inversion.
- Swelling or lump in the underarm area.
- Unexplained weight loss.
It is important to note that not all breast lumps are cancerous, and not all breast cancers cause lumps. Some breast cancers can also have no symptoms at all, which is why regular mammograms and clinical breast exams are recommended for early detection. If you notice any unusual changes in your breasts, it is important to consult with your doctor for a proper diagnosis.
How Many Stages of Breast Cancer?

Cancer is staged according to the size of the tumor and whether it has spread to lymph nodes or other parts of the body.
There are different ways of staging breast cancer. One way is from stage 0 to 4, but these may be broken down into smaller stages.
- Stage 0: Known as ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), the cells are limited to within a duct and have not invaded surrounding tissues.
- Stage 1: At the beginning of this stage, the tumor is up to 2 centimeters (cm) across and it has not affected any lymph nodes.
- Stage 2: The tumor is 2 cm across and it has started to spread to nearby nodes.
- Stage 3: The tumor is up to 5 cm across and it may have spread to some lymph nodes.
- Stage 4: The cancer has spread to distant organs, especially the bones, liver, brain, or lungs.
Learn More About Breast Cancer Stages.
Risk factors of Breast Cancer
There are many factors that can increase the risk of developing breast cancer. Some of the common risk factors include:
Gender: Women are more likely to develop breast cancer than men.
Age: The risk of breast cancer increases with age, especially after age 50.
Family history: Women who have a family history of breast cancer, especially a first-degree relative (mother, sister, or daughter) with the disease, are at higher risk.
Genetic mutations: Inherited mutations in certain genes, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, can increase the risk of breast cancer.
Personal history: Women who have had breast cancer or certain non-cancerous breast conditions are at higher risk.
Hormonal factors: Women who began menstruating before age 12, had menopause after age 55, or have never been pregnant are at higher risk.
Lifestyle factors: Obesity, lack of physical activity, and excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of breast cancer.
Radiation exposure: Previous radiation therapy to the chest area can increase the risk of breast cancer.
It is important to note that having one or more of these risk factors does not mean that a person will develop breast cancer, and many women who develop breast cancer have no known risk factors.
How to Diagnosis breast cancer?
There are several ways to diagnose breast cancer, including:
Mammogram: A mammogram is an X-ray of the breast that can detect lumps or abnormalities that may be indicative of breast cancer.
Breast ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of the breast tissue and can be used to determine whether a lump is a solid mass or a fluid-filled cyst.
Breast Ultrasound / MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses radio waves and a strong magnet to create detailed images of the breast tissue. It is typically used to evaluate the extent of the cancer in the breast and surrounding tissue.
Biopsy: A biopsy involves removing a sample of breast tissue for testing in a laboratory to determine if it is cancerous.
Physical exam: A healthcare provider can perform a physical exam of the breast tissue to check for lumps, changes in shape or size, or other abnormalities.
Genetic testing: Genetic testing can identify mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes that increase a person’s risk of developing breast cancer.
If a diagnosis of breast cancer is made, additional tests may be performed to determine the extent (stage) of the cancer and whether it has spread to other parts of the body. These tests may include a chest X-ray, bone scan, CT scan, or PET scan.
Treatment for Breast Cancer
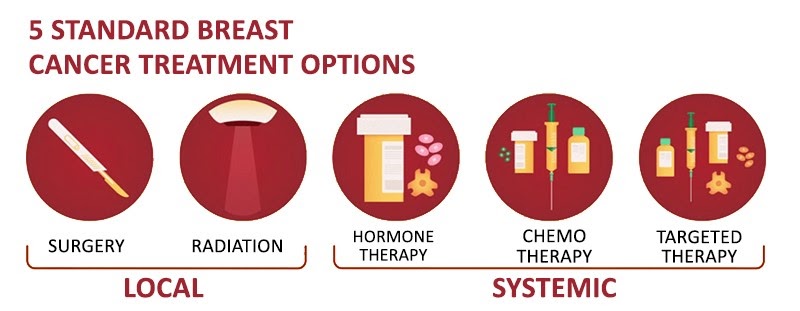
Your doctor will determines the best possible treatment options based on your types of Breast cancer, its grade, size and stage, and whether the cancer cells are sensitive to hormones.
Most women undergo surgery for breast cancer and many also receive additional treatment after surgery, such as Radiation therapy, chemotherapy and hormone therapy. Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy might also be used before surgery in certain situations.
There are many options for breast cancer treatment, and you may feel overwhelmed as you make complex decisions about your treatment. Consider seeking a second opinion from a breast specialist in a breast center or clinic. Talk to other women who have faced the same decision.
Breast Cancer Surgery
Operations used to treat breast cancer include:
- Removing the breast cancer (lumpectomy). During a lumpectomy, which may be referred to as breast-conserving surgery or wide local excision, Your surgeon removes the tumor and a small margin of surrounding healthy tissue.
A lumpectomy may be recommended for removing smaller tumors. Some people with larger tumors may undergo chemotherapy before surgery to shrink a tumor and make it possible to remove completely with a lumpectomy procedure.
- Removing the entire breast (mastectomy). A mastectomy is an operation to remove all of your breast tissue. Most mastectomy procedures remove all of the breast tissue — the lobules, ducts, fatty tissue and some skin, including the nipple and areola (total or simple mastectomy).
Newer surgical techniques may be an option in selected cases in order to improve the appearance of the breast. Skin-sparing mastectomy and nipple-sparing mastectomy are increasingly common operations for breast cancer.
- Removing a limited number of lymph nodes (sentinel node biopsy). To determine whether cancer has spread to your lymph nodes, your surgeon will discuss with you the role of removing the lymph nodes that are the first to receive the lymph drainage from your tumor.
If no cancer is found in those lymph nodes, the chance of finding cancer in any of the remaining lymph nodes is small and no other nodes need to be removed.
- Removing several lymph nodes (axillary lymph node dissection). If cancer is found in the sentinel lymph nodes, your surgeon will discuss with you the role of removing additional lymph nodes in your armpit.
- Removing both breasts. Some women with cancer in one breast may choose to have their other (healthy) breast removed (contralateral prophylactic mastectomy) if they have a very increased risk of cancer in the other breast because of a genetic predisposition or strong family history.
Most women with breast cancer in one breast will never develop cancer in the other breast. Discuss your breast cancer risk with your doctor, along with the benefits and risks of this procedure.
Complications of breast cancer surgery depend on the procedures you choose. Breast cancer surgery carries a risk of pain, bleeding, infection and arm swelling (lymphedema).
You may choose to have breast reconstruction after surgery. Discuss your options and preferences with your surgeon.
Consider a referral to a plastic surgeon before your breast cancer surgery. Your options may include reconstruction with a breast implant (silicone or water) or reconstruction using your own tissue. These operations can be performed at the time of your mastectomy or at a later date.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy for breast cancer is a treatment that uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells in the breast tissue. It is typically given after surgery to remove the tumor, and may also be used in combination with chemotherapy. The goal of radiation therapy is to destroy any remaining cancer cells in the breast tissue that may not have been removed during surgery.
Radiation therapy for breast cancer is typically delivered externally, using a machine called a linear accelerator. The radiation is carefully targeted to the affected breast tissue, while minimizing exposure to surrounding healthy tissue. Treatment usually lasts for several weeks, with daily radiation sessions that take just a few minutes each. In some cases, radiation therapy may also be used before surgery to shrink a large tumor, making it easier to remove. This is known as neoadjuvant radiation therapy.
Radiation therapy for breast cancer may cause side effects, such as fatigue, skin irritation or changes, and changes in the breast tissue or chest wall. These side effects are usually temporary and can be managed with medication or other supportive care.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to destroy fast-growing cells, such as cancer cells. If your cancer has a high risk of returning or spreading to another part of your body, your doctor may recommend chemotherapy after surgery to decrease the chance that the cancer will recur.
Chemotherapy is sometimes given before surgery in women with larger breast tumors. The goal is to shrink a tumor to a size that makes it easier to remove with surgery.
Chemotherapy is also used in women whose cancer has already spread to other parts of the body. Chemotherapy may be recommended to try to control the cancer and decrease any symptoms the cancer is causing.
Chemotherapy side effects depend on the drugs you receive. Common side effects include hair loss, nausea, vomiting, fatigue and an increased risk of developing an infection. Rare side effects can include premature menopause, infertility (if premenopausal), damage to the heart and kidneys, nerve damage, and, very rarely, blood cell cancer.
Hormone therapy
Hormone therapy (also called hormonal therapy, hormone treatment, or endocrine therapy) slows or stops the growth of hormone-sensitive tumors by blocking the body’s ability to produce hormones or by interfering with hormone action. Tumors that are hormone-insensitive do not respond to hormone therapy.
Hormone therapy for breast cancer is not the same as menopausal hormone therapy or female hormone replacement, in which hormones are given to reduce the symptoms of menopause.
Hormone therapy side effects depend on your specific treatment, but may include hot flashes, night sweats and vaginal dryness. More serious side effects include a risk of bone thinning and blood clots.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted drug treatments attack specific abnormalities within cancer cells. As an example, several targeted therapy drugs focus on a protein that some breast cancer cells overproduce called human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). The protein helps breast cancer cells grow and survive. By targeting cells that make too much HER2, the drugs can damage cancer cells while sparing healthy cells.
Targeted therapy drugs that focus on other abnormalities within cancer cells are available. And targeted therapy is an active area of cancer research.
Your cancer cells may be tested to see whether you might benefit from targeted therapy drugs. Some medications are used after surgery to reduce the risk that the cancer will return. Others are used in cases of advanced breast cancer to slow the growth of the tumor.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy uses your immune system to fight cancer. Your body’s disease-fighting immune system may not attack your cancer because the cancer cells produce proteins that blind the immune system cells. Immunotherapy works by interfering with that process.
Immunotherapy might be an option if you have triple-negative breast cancer, which means that the cancer cells don’t have receptors for estrogen, progesterone or HER2. For triple-negative breast cancer, immunotherapy is combined with chemotherapy to treat advanced cancer that’s spread to other parts of the body.
Frequently Asked Questions About Breast Cancer
Q: How long is the duration of breast cancer treatment?
A: The duration of breast cancer treatment depends on the stage of cancer. For early-stage breast cancer, chemotherapy typically lasts for three to six months, but the treatment duration may vary based on individual circumstances. Advanced breast cancer may require treatment for more than six months.
Q: What is the duration of chemotherapy for breast cancer?
A: Chemotherapy cycles for breast cancer are usually two or three weeks long, but the duration may vary depending on the medication used. Some medications are given only on the first day of the cycle, while others are administered once a week for a few weeks or once every other week.
Q: Can breast cancer be cured completely?
A: There is no natural cure for breast cancer. Medical therapies are required to eliminate, reduce, or slow the growth of tumors. However, alternative therapies and lifestyle changes can be used in addition to medical treatments to help control breast cancer symptoms.
Q: How long after a breast cancer diagnosis is surgery scheduled?
A: In general, surgery is scheduled within 90 days after a breast cancer diagnosis. There are three surgical procedures commonly used to treat breast cancer: lumpectomy, mastectomy, and lymph node removal.
Q: Can breast cancer spread while waiting for surgery?
A: It is unclear whether short-term delays before surgery allow a woman’s tumor to develop and spread. However, a recent study of 818 patients found no evidence that a modest delay before surgery allowed breast cancer to develop and spread.
Q: What is the best approach to reducing the risk of breast cancer?
A: Early detection is key to successful treatment of breast cancer. Women with a family history of breast cancer, those over age 40, or those experiencing symptoms should have mammograms at least once every two years. While there is no guaranteed way to prevent breast cancer, healthy lifestyle habits like regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption can reduce the risk.
Q: Do I need to follow a specific diet after breast cancer treatment?
A: Breast cancer surgery is a significant surgical procedure, and dietary restrictions may be necessary. However, a specific diet can only be prescribed by a dietitian based on individual needs and circumstances.
Top 10 Breast Cancer Doctors in India
- Dr Vinod Raina
- Dr. Ashok Vaid
- Dr Randeep Singh
- Dr. Hari Goyal
- Dr Niranjan Naik
- Dr Priya Tiwari
- Dr. Surender Kumar Dabas
- Dr Kapil Kumar
- Dr. Nitin Leekha
- Dr. Durgatosh Pandey
Top 10 Surgical Oncologist In India
Top 10 Breast Cancer Hospital in India
- Medanta – The Medicity, Gurgaon
- Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurgaon
- BLK Super Speciality Hospital, New Delhi
- Artemis Hospital, Gurgaon
- Indraprastha Apollo Hospital, New Delhi
- Max Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
- Manipal Hospitals Dwarka, Delhi
- Dharamshila Narayana Superspeciality Hospital , New Delhi
- Fortis Hospital, Mulund, Mumbai
- Rajiv Gandhi Cancer Institute and Research Centre, New Delhi
