Discectomy Surgery Cost in India
The average cost of Discectomy Surgery in India starts from $3,500 to $5,000. The cost can be less or more depending on several factors including your medical condition, surgeon practice and hospital location.
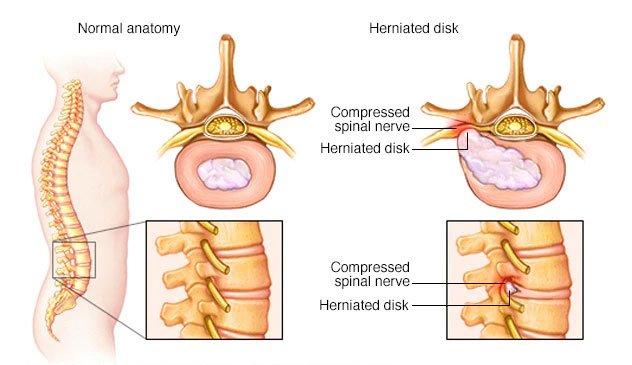
What is Discectomy?
Discectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the damaged portion of a herniated disc in your spine. the nerves nearby a herniated disc can irritate or compress. Discectomy surgery is the most common and successful for treating pain that radiates down your arms or legs.
The procedure is less helpful for treating actual back pain or neck pain. Most people who have back pain or neck pain find relief with more-conservative treatments, such as physical therapy.
Your surgeons may recommend discectomy if traditional, nonsurgical treatment haven’t worked or if your symptoms worsen. There are several ways to perform a discectomy. Many surgeons now prefer minimally invasive discectomy, which uses small cut and a tiny video camera for viewing the procedure.
Why it's done
A discectomy is performed to relieve the pressure a herniated disk (also called a slipped, ruptured or bulging disc or disc prolapse) places on a spinal nerve. A herniated disc occurs when some of the softer material inside the disc pushes out through a crack in the tougher exterior.
Your doctor may recommend discectomy if:
- You are facing problem in walking and standing because of nerve weakness
- When non-Surgical treatment fails to improve your symptoms, such as medicine, physical therapy, and steroid injection.
- Pain radiating into your buttocks, legs, arms or chest becomes too much to manage
What are the types of discectomy?
There are three ways a surgeon may choose to perform a discectomy:
1. Open or conventional discectomy in which the surgeon makes a comparatively large incision to allow clear vision and also removes some muscle and ligament.
2. Microdiscectomy is minimally invasive with a tiny incision. The surgeon does not remove any muscle or bone, but inserts a tube with a tiny camera/instrument to remove the damaged portion of the disc.
3. Laser discectomy is in wider use now. This procedure requires no incision. Instead, the surgeon burns the prolapsed tissue away with a laser inserted through a needle.
The types of discectomy procedures include:
1. Cervical discectomy is the removal of a disc in the neck area (cervical spine).
2. Lumbar discectomy is the removal of a disc in the lower back (lumbar spine).
3. Sacral discectomy is the removal of a disc in the back between your pelvic, or hip bones (sacral spine).
4. Thoracic discectomy is the removal of a disc in the middle part of the back (thoracic spine).
Conditions That Can Benefit From Discectomy Surgery
Both traditional discectomy surgery and microdiscectomy surgery are performed to treat people who are experiencing pain, numbness, weakness, or tingling in the back, legs, or arms, caused by a herniated disc.
A herniated disc does not necessarily mean you need to get surgery. People often find that their symptoms can be treated through non-surgical options, such as rest, pain medication, or physical therapy.
But, patients who have failed to achieve significant relief from their symptoms after six to twelve weeks of nonsurgical treatment may benefit from a discectomy procedure. Microdiscectomies have been shown to be a safe and effective treatment option when nonsurgical intervention has proven ineffective.
Who needs Discectomy Surgery?
Discectomy surgery is commonly recommended for the following conditions:
- When a herniated disc is present.
- When significant weakness, pain or numbness in legs or feet.
- When the leg pain experience is worse than the back pain (sciatica).
- Symptoms do not improve with medication of physical therapy.
- Symptoms that have not improved with physical therapy or medication.
- If the pain or weakness is combined with bladder or bowel control issues and/or a loss of feeling in the genitals.
- When a patient is diagnosed with degenerative disc disease.
Risks and Complications
Discectomy is considered a safe procedure. But as with any surgery, discectomy carries a risk of complications. Potential complications include:
- Bleeding
- Pain
- Infection
- Leaking spinal fluid
- Injury to blood vessels or nerves in and around the spine
Diagnosis for Discectomy
X-ray: An X-rays required for vertebrates and joints a clear picture of the problem for the same.
Computed tomography (CT/CAT scan): CT/CAT scan are used to get detailed images of the spinal canal and surrounding structures.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): An MRI produces 3-D images of the spinal cord and nerve roots, as well as the discs themselves.
Electromyography or nerve conduction studies (EMG/NCS): An Electromyography or NCS is used to measure electrical impulses along nerves and muscles.
Myelogram: This test uses contrast dye into the spinal fluid space (cerebrospinal fluid) to outline the nerves and detect pathology of the spinal cord.
How do you prepare before Discectomy?
You can gather information and read-up about the discectomy procedure during this preparative period. In case of any doubts, the you should talk to the surgeon, Once a decision is made to go for the discectomy surgery. The discectomy procedure is done either by an orthopedic surgeon or a neurosurgeon.
- The surgeon may carry out a thorough physical examination to assess that the patient is in the healthy condition to have the surgery.
- Discectomy is a major procedure and it is important to get all doubts and fears clarified by the doctor. If necessary, a second opinion may be sought.
- The surgeon will ensure the state of health of the patient and rule out any chronic underlying diseases through blood and urine analysis.
- If the patient is a smoker, smoking should be stopped several days before the surgery or quit altogether.
- Certain medications such as warfarin and/or aspirin that the patient may be taking will be stopped by the surgeon approximately 2 weeks prior to the surgery. These medications increase the risk of bleeding during surgery.
- The patient will be evaluated with the results of these investigations by the cardiologist and anesthetist and pronounced fit for surgery provided there are no serious problems.
- The patient is advised to get admitted to the hospital on the evening before surgery for the administration of certain medications and to perform certain routine blood tests.
- The patient should be on an empty stomach since midnight the previous night.
- On the morning of the surgery, the site of operation is cleaned and any hair over the area is shaved.
- The patient is provided a clean surgical gown to wear and taken to the operation theater.
What Happens During the Discectomy Procedure?
Before the surgery, the patient may be made unconscious by administering general anesthesia (GA) or the lower part of the body from the back down may be numbed by spinal anesthesia. Local anesthesia is not recommended for this type of surgery.
Once the patient is anesthetized, he is turned over to lie down on the front (prone position) with appropriate padding.
The patient’s back is scrubbed with sterile soap so that a sterile field is created, which is then draped before the surgery begins.
A small cut (incision) is made over the region where the disc is herniated. The affected part of the spine is exposed by splitting the muscles from the bones of the spine using dilators and retractors.
In the next step, a small piece of bone from the vertebra, called lamina, is removed (laminotomy or laminectomy), which creates a small window through which the spinal nerves can be visualized.
Once the ruptured disc is identified, it is removed along with other fragments of the disc that may have been dislodged or likely to get dislodged.
The layers of tissue are then sutured and finally the skin incision is sutured.
At the end of the surgery, a dressing is applied over the incision.
What Happens after the Discectomy?
After the surgery, the patient is shifted to the recovery room and the vital signs are monitored for a few hours. If they remain stable, the patient will be shifted to his room.
After the anesthesia wears off, the patient will be given clear fluids.
When normal bowel function returns, a solid diet will be provided, which usually requires 2 days post-surgery.
The following day, the patient will be encouraged to sit in a chair for about 20 minutes. Sitting and walking should be limited to 20 minutes to avoid straining the back.
Prescribed painkillers should be taken to ease the pain. Physical therapy will begin 1 to 2 days after surgery.
Results
Discectomy reduces herniated disk symptoms in most people who have clear signs of nerve compression, such as radiating pain. However, discectomy may not be a permanent cure, because it doesn’t do anything to reverse the process that allowed the disc to become herniated in the first place.
To avoid re-injuring your spine, your doctor may recommend weight loss, prescribe a low-impact exercise program, and ask that you limit some activities that involve extensive or repetitive bending, twisting or lifting.
What are the steps to be taken for Recovery after Discectomy?
During the recovery period, the patient should continue to wear the braces, and should avoid driving for at least 6 weeks, due to both safety and legal reasons. The patient should desist from picking-up objects from the floor by bending at the waist. Instead, bending at the knees is advised, if required. Carrying heavy objects must be avoided. The incision should be kept dry to avoid infections. Sponge baths are recommended until the doctor advises to take regular baths. Some other important aspects that should be kept in mind during recovery include the following:
1. Sitting: Maintaining a sitting posture may be difficult at first. The sitting period can be 20 minutes initially, which can be increased gradually.
2. Walking: Walking is encouraged during the recovery period, but it is important not to get overtired. Climbing stairs, if absolutely necessary, should be limited to once daily. Walking will enable regaining mobility quicker and also reduce chances of scar tissue formation.
3. Rehabilitation: For those intending to return to daily activities, a rehabilitation program, as advised by the doctor, will continue at home, including physical therapy by a qualified physiotherapist.
4. Returning to work: The aim of recovery is to return to normal daily activities which includes returning to work. If engaged in a sedentary job in an office setting, the patient can usually return to work within 2-4 weeks post-surgery. If engaged in manual work involving operation of machinery, joining work may take up to 6-8 weeks. As a general rule, the patient should not return to work without the doctor’s permission.
Frequently asked questions about Discectomy Surgery
Q. How much does Discectomy Surgery Cost in India?
A. The average cost of Discectomy Surgery in India starts from $3,500 (INR 247,038). The cost can be less or more depending on several factors including your medical condition, experience of the surgeon and the type of hospital you choose.
Q. How long is a discectomy surgery?
A. It may take about 1 hour. Here is an example of what you might expect: You will receive a local anesthetic so that you won’t feel any pain or discomfort during the procedure.
Q. Can you walk after herniated disc surgery?
A. You will be encouraged to slowly increase your activity level during the first week of recovery after surgery for a herniated disc. Walking is a great exercise after surgery as it helps to improve aerobic endurance and promote circulation in your body.
Q. What is the success rate of a discectomy?
A. The success rate for discectomy spine surgery is generally high, with one extensive medical study showing good or excellent results overall for 90% of people who have the procedure.
