Best Liver Transplant Cost In India
What is the Liver Transplant Cost in India?
The cost of a liver transplant in India can range anywhere between 22000-45000 USD. This includes recipient and donor pre-transplant evaluation, the surgery itself and the post-surgery recovery period. There are certain factors that affect the cost of an organ transplant. liver transplant cost depends on surgeon charges, hospitals location and the most impartment is compatible of patient and donor.
How to check compatibility of recipient and donor?
Blood group should be same.
Patient weight should be 50-60kg.
Liver size of donor.
Overview
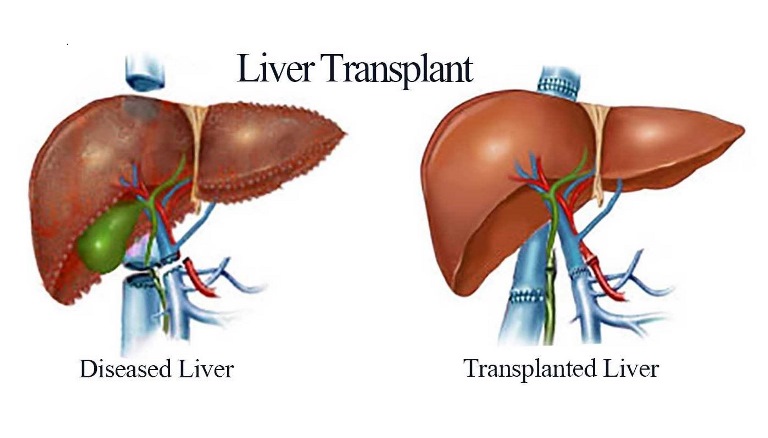
A liver transplant is a surgery to replace a diseased liver with a healthy liver from another person. A whole liver may be transplanted, or just part of one. In most cases the healthy liver will come from an organ donor who is brain dead.
The liver is the only organ in the body that can replace lost or injured tissue (regenerate). The donor’s liver will soon grow back to normal size after surgery. The part that is received as a new liver will also grow to normal size in a few weeks.
Why it's done
Liver transplant is a treatment option for some people with liver failure and for people with liver cancer whose condition can’t be controlled with other surgeries and medical treatment.
Liver failure may happen quickly or over a long period of time. Liver failure that occurs quickly, in a matter of weeks, is called acute liver failure. Acute liver failure is an uncommon condition that is usually the result of complications from certain medications.
Although a liver transplant may treat acute liver failure, it is more often used to treat chronic liver failure. Chronic liver failure occurs slowly over months and years.
Chronic liver failure may be caused by a variety of conditions. The most common cause of chronic liver failure is scarring of the liver (cirrhosis). When cirrhosis occurs, scar tissue replaces typical liver tissue and the liver doesn’t function properly. Cirrhosis is the most frequent reason for a liver transplant.
Major causes of cirrhosis leading to liver failure and liver transplant include:
- Hepatitis B and C.
- Alcoholic liver disease, which causes damage to the liver due to excessive alcohol consumption.
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, a condition in which fat builds up in the liver, causing inflammation or liver cell damage.
Genetic diseases affecting the liver. They include hemochromatosis, which causes excessive iron buildup in the liver, and Wilson’s disease, which causes excessive copper buildup in the liver. - Diseases that affect the tubes that carry bile away from the liver (bile ducts). They include primary biliary cirrhosis, primary sclerosing cholangitis and biliary atresia. Biliary atresia is the most common reason for liver transplant among children.
Risk and Complications
To allow the transplanted liver to survive in a new body, the given medications should be taken regularly. The most common symptoms of rejections are fever, jaundice, dark urine, itching, fatigue or irritability, nausea and headache.
The two most common complications following liver transplant are rejection and infection
1.Infection: Because anti-rejection drugs that suppress our immune system are needed to prevent the liver from being rejected, our body will be at an increased risk for infections. This problem diminishes as time passes. Not all patients have problem with infections, most infections can be treated successfully as they occur.
2.Rejection: Our immune system works to destroy foreign substances that invade our body. The immune system, however cannot distinguish between our transplanted liver and unwanted invaders, such as viruses and bacteria. Therefore, our immune system may attempt to attack and destroy our new liver. This is called rejection episode. About 70% of all liver-transplant patients have some degree of organ rejection prior to discharge. Anti-rejection medications are given to ward off the immune attack.
What are the symptoms?
There are no visible signs in the early stages of primary Liver cancer. Liver cancer treatment begins once a person has fallen sick critically owing to liver damage. The standard signs and symptoms of liver cancer may include the following-
Yellowing of the skin, eyes, and tongue commonly known as Jaundice it is one of the most common indications that implies Liver cancer.
- Abdominal pain
- Sudden loss of weight
- Swollen abdomen due to enlarging of liver
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Vomiting sensation
- Having fever constantly is a usual sign that one shouldn’t ignore
These symptoms are known as nonspecific symptoms, as other chronic disorders may trigger similar effects. These symptoms remain inactive in the early stages and when they surface, the disease becomes virtually uncontrollable.
Which Tests Are Required Before Getting a Liver Transplant?
When the doctor suggests a liver transplant to any person then the doctors will ask for all the pervious medical records, X-rays, liver biopsy slides, operative reports if any and a record of medications to the pre-evaluation. To match and to update the previous tests.
- Blood tests to determine blood type, clotting ability, and biochemical status of blood, and to gauge liver function. Serology screening is also included.
- Doppler ultrasound: to determine if the blood vessels to and from they liver are open.
- CT scan: Computed tomography uses X-rays and a computer to generate pictures of the liver, showing its size and shape.
- Echocardiogram and stress testing to help evaluate your heart.
- Pulmonary function studies to determine the lungs ability to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- Biopsy and Review the pervious Block or Slide to recognize the present condition of the diseases.
- Human leukocyte antigen ( HLA Matching), typing is a method to determine how closely the tissues of one person match the tissues of another person. most likely place to find an HLA match between two people is among siblings who have the same mother and father.
Types of Liver Transplant Donor
1.Deceased organ donation transplant – involves transplanting a liver that has been removed from a person who died recently
2.Living donor liver transplant – a section of liver is removed from a living donor; because the liver can regenerate itself, both the transplanted section and the remaining section of the donor’s liver are able to regrow into a normal-sized liver
3.Split donation transplant – a liver is removed from a person who died recently and is split into two pieces; each piece is transplanted into a different person, where they will grow to a normal size
Criteria for Liver Donation for a Donor?
- A Donor must be willing to donate and must be aged between 18-55 years.
- The weight must be 50-85 kg.
- The donor should be a first relative or member of the family.
- The blood group of both donor and recipient must be identical/matching.
- All the body parts of the donor must be functioning properly.
- Satisfactory volume of liver must be available for the recipient while partial liver of the donor is used.
- The appropriateness of the donor for the liver donation would be confirmed by the Liver Transplant Team after revising the above declared characteristics and medical diagnosis.
Documents needed for Liver Transplantation (International)
Donor related other than spouse.
- Photo identify proof (passport, medical visa, if tourist visa then it need to be converted into medical visa etc) of the patient and the donor.
- Birth certificate /school certificate of the patient and the donor.
- 1t6 passport size photograph of the patient and the donor.
- 3 passport size photograph of the immediate relatives of the donor.
- DNA profiling of the patient and the donor.
- Psychiatry evaluation of donor from Hospital.
- NOC from the embassy in India
Pre-Operative Evaluation Process For Liver Transplantation
As liver transplantation is a large step, so, one must embrace a positive mindset before becoming treated. The test is a step-by-step procedure that starts with the receiver’s evaluation. When the individual is qualified for transplantation, the search for donors at the household starts based on their own blood collection.
If the donor is located, it requires clearance from the consent committee to move farther and the transplantation generally goes in about 2-3 weeks.
Measure 1: Pre-transplant Recipient Evaluation
- After the individual is diagnosed with coronary artery disease disorder and needing the transplant, the transplant group performs a set of evaluation tests like blood tests, CT scans along with other tests to look at the operation of their lungs, heart and other organs.
- The test generally takes 7-10 days that’s an inpatient procedure.
Measure 2: To Pick The Donor
- Selecting the donor has become the most crucial portion of the full procedure. The donor must fulfill these standards:
- A relative related by blood according to the Act.
- When the contributor is non-related by the bloodstream, then it requires approval by the government-appointed authorization committee together with clarifying that there’s not any industrial angle involved.
- Age set between 18-55 years without any obese difficulties.
- The donor’s liver dimensions ought to be sufficient enough to give the needed sum of the portion.
Compatible blood collection together with the receiver - Additionally, it has HLA testing and fitting to be performed prior to the consent committee meeting.
Together with the above-mentioned procedure, the individual and the family needs to manage the remedy emotionally, mentally, and financially. Thus, they need to be powerful enough to cope with this type of circumstance. Reach out to our experts for the best & affordable liver transplant cost in India.
Types of Liver Transplant Procedure:
1.Orthotopic Transplantation:- In this procedure the receipient’s diseased liver is completely replaced with the healthy liver.
2.Heterotopic Transplantation:- In this procedure, the diseased liver is kept remain intact at its place and donor’s liver is placed at the nearest site to the diseased liver. This procedure is performed when the doctor is of the opinion that the diseased liver might recover, if the liver recovers, the other organ shrivels away, if not, then the original one shrivels and the donor liver performs the body functions.
3.Reduced-size Liver Transplantation:- This procedure is generally performed on children and involves the transplanting a part of the healthy donor liver into a patient. This procedure is performed when 15-20% of the original liver is intact. This way, one donor liver can be used for two successful transplants.
Liver Transplant Procedure
- The surgery usually takes between five and six hours, but may be longer or shorter due to the difficulty of the operation and the experience of the surgeon.
- Liver Transplantation is performed under a general anesthesia.
- Before the surgery, a tube is placed through the mouth of patient into windpipe to help breathe during the operation.
- A Y-shaped incision in the abdomen is made and the diseased liver is removed. Donated liver is then inserted and attached to the major blood vessels and to the bile ducts. The incision is then closed at the end of surgery.
- Entire procedure of liver transplantation surgery usually takes about 6-12 hour to perform successfully.
After your liver transplant, you can expect to:
Possibly stay in the intensive care unit for a few days. Doctors and nurses will monitor your condition to watch for signs of complications. They’ll also test your liver function frequently for signs that your new liver is working.
Spend 5-10 days in the hospital. Once you’re stable, you’re taken to a transplant recovery area to continue recuperating.
Have frequent checkups as you continue recovering at home. Your transplant team designs a checkup schedule for you. You may undergo blood tests a few times each week at first and then less often over time.
Take medications for the rest of your life. You’ll take a number of medications after your liver transplant, many for the rest of your life. Drugs called immunosuppressants help keep your immune system from attacking your new liver. Other drugs help reduce the risk of other complications after your transplant.
When Will I Be Able to Go Home After a Liver Transplant
The average hospital stay after a liver transplant is 2 weeks to 3 weeks. Some patients may be discharged in less time, while others may be in the hospital much longer, depending on the complications that arise to the patients.
Discharge instructions for liver transplant
You must be able to get out of bed, walk, eat, and shower on your own
You must demonstrate understanding of your medication regimen
Your incisions must be healing normally
You must have an acceptable blood level of your primary immunosuppressive medication. This will usually be tacromilus (Prograf), but occasionally others are prescribed.
Self Care
Rest as needed. Slowly start to do more each day. Return to your daily activities as directed.
Drink liquids as directed. Ask how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you.
Eat a variety of healthy foods. Healthy foods include fruits, vegetables, whole-grain breads, low-fat dairy products, beans, lean meats, and fish. Ask if you need to be on a special or low-salt diet.
Maintain a healthy weight. Ask how much you should weigh. Ask your healthcare provider to help you create a weight loss plan if you are overweight.
Exercise as directed. Ask about the best exercise plan for you. This may help increase your energy levels and help you feel better.
Do not drink alcohol or use tobacco products. Alcohol and tobacco can harm your new liver. Ask for information if you currently drink alcohol or use tobacco products and need help quitting.
Frequently Asked Questions for Liver Transplant?
Q. What is the success rate of liver transplant in India?
A. The success rate of Liver transplant in India has been 90%. But like any other transplant, liver transplant has its very own risks and complication.
Q. How long can a person live with a liver transplant In India?
A. In general, about 75% of people who undergo liver transplant live for at least five years. That means that for every 100 people who receive a liver transplant for any reason, about 70 will live for five years and 30 will die within five years
Q. Who can donate for liver transplant in India?
A. The living liver donor should be a 18-55 years old, willing and healthy family person weighing between 50-85 kg, should not be overweight or obese (since such people tend to have fatty livers that may not work well in the recipient), and should have either the same blood group as the patient’s or blood group “O”
Q. Why should you go for Liver Transplantation in India?
A. In the past few years, the liver transplant technology and technique have progressed in India and is not a usual procedure accessible across the country. The survival rate is at par with the best across the globe. India has some of the top hospitals for a liver transplant with the best current technology and state-of-the-art infrastructure. India is a very viable option for undertaking the treatment primarily because of the highly reasonable cost for the procedure. India has many experienced doctors and surgeons who have established their top-notch credibility.
Q. Is there an age limit for liver transplantation?
The age limit is individualized as it varies with a patient’s overall health condition. However, it is rare to offer liver transplant to someone greater than 70 years old.
Q. What are the risks of being a live liver donor?
Even though live liver donation is considered a very safe operation, it involves major surgery and is associated with complications, which may include:
Possible allergic reaction to anesthesia
Pain and discomfort
Nausea
Wound infection
Bleeding that may require transfusion
Blood clots
Pneumonia
Bile leakage, bile duct problems
Hernia
Scar tissue formation
India has constantly been a top destination in offering the best healthcare treatment. Indian hospitals comprise of highly qualified doctors with lots of experience in treating patients from all over the world. It is vital for end-stage liver disease patients to undergo treatment under the help of a highly experienced surgeon. Getting a skilled surgeon for liver transplant in India is not that hard as the hospitals in the country pay exceptional attention to hiring surgeons who are qualified from some of the topmost health institutions in the world.
A liver transplant, is the treatment of choice in case a person’s liver fails to function permanently. The procedure involves surgical removal and replacement of the diseased liver with whole or part of a liver donated by another person whether alive or deceased.
Best Liver Transplant Surgeon In India

Dr Arvinder Singh
Chairman , MBBS, MS, FRCS, FRCS 30 Years of Experience Gurgaon, India

Dr Vivek Vij
Director , MBBS, MS, DNB 17 Years of Experience New Delhi , India

Dr Subhash Gupta
Chairman , Fellowship, MS, MBBS 37 years of experience New Delhi , India



